價格:免費
檔案大小:8.8 MB
版本需求:需要 iOS 6.1 或以上版本。與 iPhone、iPad 及 iPod touch 相容。
支援語言:英語

The blood pressure rises to 160/95 shortly after induction. Your 7-month old patient has already received more than enough muscle relaxant. Administering a large bolus of fentanyl does nothing. Even an attempt to deepen anesthesia fails to control the BP’s upward trend. As you now glance at the ECG tracing on the monitor, you notice that the ST segments are starting to sag downwards. With an inward sigh, you realize this is not going to be a routine circumcision…
Pediatric anesthesiologists are no strangers to managing emergency situations. Of course, experienced attendings manage uncomplicated laryngospasm or mild bradycardia, for example, on a routine basis without breaking a sweat. Certain crises however arise so infrequently that individual practitioners experience them personally only a few times within their professional lifetimes. Under such circumstances it can be hard to recall full details of all necessary facts, decision points and management steps.
The Society for Pediatric Anesthesia (SPA) Quality and Safety Committee has recently completed a two-year project to address just these challenges. Inspired by ultra-safe industries like aviation and nuclear power generation, the committee created a compendium of crisis checklists for consultation in the pediatric OR at the first hint of trouble.
The committee chose 17 challenging emergency problems for this treatment. Members divided the list between institutions from across the nation. The algorithms were adapted into this application by a multi-disciplinary team at The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
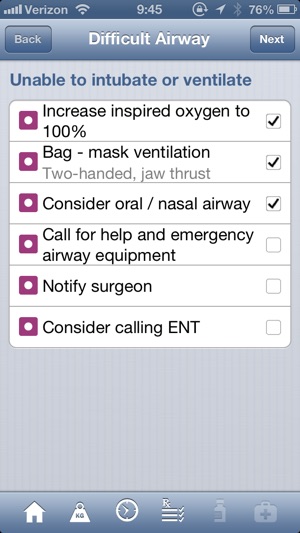
Each checklist starts by summarizing the problem it addresses, and then lists relevant factors to consider and possible steps to take in the event of that particular emergency.
The checklists include drugs treatments if appropriate, along with a handy weight-based dosie calculator.
The full list of topics covered by the checklists is:
•Air embolism
•Anaphylaxis
•Bradycardia
•Cardiac arrest
•Difficult airway
•Fire (airway and OR)
•Hyperkalemia

•Hypertension
•Hypotension
•Local anesthetic toxicity
•Loss of evoked potentials
•Malignant hyperthermia
•Myocardial ischemia
•Tachycardia
•Tension pneumothorax
•Transfusion and reactions
•Trauma
•Head trauma
Additional Features:
•Built-in timer to keep track of actions in the event
•Built-in log timestamps actions to assist in debriefing and education
•Malignant Hyperthermia calculator
•Glasgow Coma Scale calculator

支援平台:iPhone, iPad
